The best magic of all, is the magic that is real. (James TURRELL)
Tricks of the Eye
You can be fooled by your eyes, or you can fool your eyes to see things differently. Eitherway, this is an interesting exercise but it may take some effort so be patient.
The examples come from different sources, I have tried to give full credit where possible ( 21-00-photo-credits, 20-00-references, 19-00-bibliography ) but some of the examples are quite old really.
.jpg)
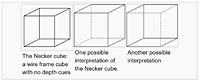
The Necker Cube
- by crystallographer Louis Albert NECKER
- 1932 Switzerland
- see also: im-possible.info for more explanation
The Necker cube is an optical illusion that was first published as a rhomboid in 1832 by Swiss crystallographer Louis Albert Necker.[1] It is a simple wire-frame, two dimensional drawing of a cube with no visual cues as to its orientation, so it can be interpreted to have either the lower-left or the upper-right square as its front side.
The Necker cube is an ambiguous drawing.
Necker cube on the left, impossible cube on the right.
Each part of the picture is ambiguous by itself, yet the human visual system picks an interpretation of each part that makes the whole consistent.
text & images: wikipedia

Turquoise
by © SeeSaw- Description:
1. Stare at the black dot in the red circle for 30 seconds - 2. Look at the black dot on the white page.
- 3. Close your eyes for a moment
- or use: 06-00b (1), 06-00b (2)
.
link:
.jpg)
.jpg)
Color Blend
by © SeeSaw- 1. Stare at the black dot in the red circle for 40 seconds.
- 2. Stare at the black dot in the purple circle for 15 seconds.
- Turn the page quickly and look at the black dot on the white surface.
- 4. Close your eyes for a moment.
Publisher's Description:
link:
.jpg)
.jpg)
90 Degree picture
by © SeeSaw- 1. Note the brightness of the circle and its ground
- 2. Switch back and forth with the next slide
- Compare the brightness again.
Publisher's Description:
link:

Publisher's Description:
link:

Publisher's Description:
link:

Publisher's Description:
link:

Publisher's Description:
link:
.jpg)
.jpg)
Publisher's Description:
link:

Red and Green Picture
by © SeeSaw- 1. Take the red and green glasses out of the envelope on the inside back cover.
- 2. Look at the picture (note: green filter for the right eye).
- 1. Take the red and green glasses out of the envelope on the inside back cover.
- 2. Look at the picture (note: red filter for the left eye).
Red and Green Panorama
Publisher's Description:
link:

Publisher's Description:
link:

Publisher's Description:
link:

Publisher's Description:
link:
Publisher's Description:
link:
